Federal Government Approves Construction for New York’s First Offshore Wind Farm
Contact Information
Permitting Council Press Office (media@permittting.gov)
The U.S. Department of the Interior’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management approved the construction and operations plan for the South Fork Wind project, marking the first offshore wind energy project to complete the Federal environmental review and authorization process, FAST-41. The Ørsted and Eversource project, the first offshore wind farm slated to deliver electricity to New York, is scheduled to begin operations at the end of 2023.
South Fork Wind participated in the Title 41 of the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation Act, or FAST-41, program. As a result, it benefitted from coordinated and transparent Federal environmental review and authorization across the Federal government. The Federal Permitting Improvement Steering Council (Permitting Council) administers the FAST-41 program and provides a more transparent, predictable, and inclusive infrastructure project review process for project sponsors and stakeholders. FAST-41 infrastructure projects can be tracked on the Federal Permitting Dashboard.
“A transparent and clear Federal review process is essential to offshore wind projects like South Fork Wind, New York’s first offshore wind farm,” said Ellen J. Crivella, Head of Permitting, Environment & Marine Affairs, Ørsted Offshore North America. “As the country advances offshore wind infrastructure to meet the Biden Administration’s 30 gigawatts by 2030 goals, certainty in reviews of projects like this will be vital to ensure the success of future clean energy development. The Permitting Council serves a critical role in promoting schedule transparency and accountability, and helps facilitate interagency dialogue to keep important infrastructure project reviews on track. We are grateful for the role the Permitting Council played in achieving a successful review and approval of the South Fork Wind Project.”
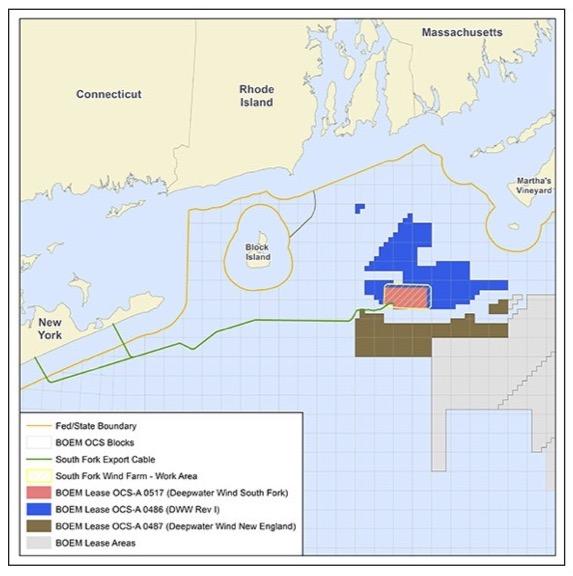
South Fork Wind is a 132-megawatt offshore wind farm that consists of 12 wind turbines and a transmission system that will generate enough clean energy to power 70,000 homes through a landfall interconnection in the town of East Hampton, New York. The offshore wind farm will be located approximately 19 miles southeast of Block Island, Rhode Island, and approximately 35 miles east of Montauk Point, New York. The project represents $740 million in economic investment and more than 1800 jobs.
“South Fork Wind will deliver clean energy to New Yorkers and help meet growing power needs in Long Island,” said Executive Director Christine Harada. “This is an incredibly important step in transitioning us to a clean energy economy and building the offshore wind industry in the country.”
The project is part of a governmentwide effort to accelerate clean energy deployment and jumpstart the U.S. offshore wind industry. It is the second offshore wind project to be authorized by the Federal government to start construction in the past year. It follows the Vineyard Wind 1 project off the coast of Massachusetts that broke ground in November of last year. The Biden-Harris administration’s goal is to deploy 30 gigawatts of offshore wind by 2030, strengthen the domestic supply chain, and create good-paying jobs.
About the Permitting Council and FAST-41
Established in 2015 by Title 41 of the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation Act (FAST-41) and made permanent in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, the Permitting Council is a unique federal agency charged with improving the transparency and predictability of the federal environmental review and authorization process for certain critical infrastructure projects. The Permitting Council is comprised of the Permitting Council Executive Director, who serves as the Council Chair; 13 federal agency Council members (including deputy secretary-level designees of the Secretaries of Agriculture, Army, Commerce, Interior, Energy, Transportation, Defense, Homeland Security, and Housing and Urban Development, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Chairs of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, Nuclear Regulatory Commission, and the Advisory Council on Historic Preservation); and the Chair of the White House Council on Environmental Quality and the Director of the Office of Management and Budget.
The Permitting Council coordinates federal environmental reviews and authorizations for projects that seek and qualify for FAST-41 coverage. FAST-41 covered projects are entitled to comprehensive permitting timetables and transparent, collaborative management of those timetables on the Federal Permitting Dashboard. FAST-41 covered projects may be in the renewable or conventional energy production, electricity transmission, energy storage, surface transportation, aviation, ports and waterways, water resource, broadband, pipelines, manufacturing, mining, carbon capture, semiconductors, artificial intelligence and machine learning, high-performance computing and advanced computer hardware and software, quantum information science and technology, data storage and data management, and cybersecurity sectors. The Permitting Council also serves as a federal center for permitting excellence, supporting federal efforts to improve infrastructure permitting including and beyond FAST-41 covered projects to the extent authorized by law, including activities that promote or provide for the efficient, timely, and predictable completion of environmental reviews and authorizations for federally-authorized infrastructure projects.
###
Last Updated: Wednesday, January 26, 2022